Earlier this month “Africa: The Big Deal Startups Deal Database” published extensive data about Africa’s startup environment by industry, geography, and investor. 1K Africa performed a trend analysis and forecast using this information that showed, among other things, that African startups have greater funding momentum than startups in several other regions.
July 11, 2022
Multiple third parties have come to similar conclusions. For example, the African Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (AVCA) found that African startups raised more in 2021 alone than in the preceding seven years combined. Specifically, in 2021 African startups raised over $4 billion; this amount equates to almost three times what was raised in 2020 and 2019.
Which Industries Saw the Most Investment in 2021?
The African startup ecosystem has been on the rise in recent years, with more and more entrepreneurs launching innovative businesses across the continent. And while there have been a number of success stories, 2021 is shaping up to be an even bigger year for African startups, with a record amount of investment flowing into the sector. So which African startup industries are seeing the most investment? Here are three that are attracting a lot of attention from investors:
- Agtech Africa is home to some of the world’s most fertile land, making it an ideal destination for agtech startups. These companies are developing innovative solutions to help farmers improve yields, reduce wastage, and better manage their resources. And they’re already starting to see significant traction, with several agtech startups raising millions of dollars in funding this year.
- Fintech Fintech is another area where Africa is seeing a lot of activity, as startups look to provide financial services to the many underserved communities across the continent. From mobile money platforms to digital banking solutions, there are a number of interesting fintech startups emerging in Africa that are attracting attention from investors.
- Edutech With over 60% of Africa’s population under the age of 25, edutech is seen as one of the continent’s most promising sectors. Startups in this space are focused on providing affordable and accessible education solutions, whether it’s online courses or educational games. And given the growing demand for quality education across Africa, it’s no surprise that edutech startups are receiving significant interest from investors.
Given that Africa has the most uncultivated arable land on earth, it is not surprising that Agriculture & Food had the second most investments: almost 10%. Surprisingly, Telecom/Media/Entertainment accounted for less than 1%. Education & Jobs accounted for approximately 6%. The graph below provides greater detail by industry.
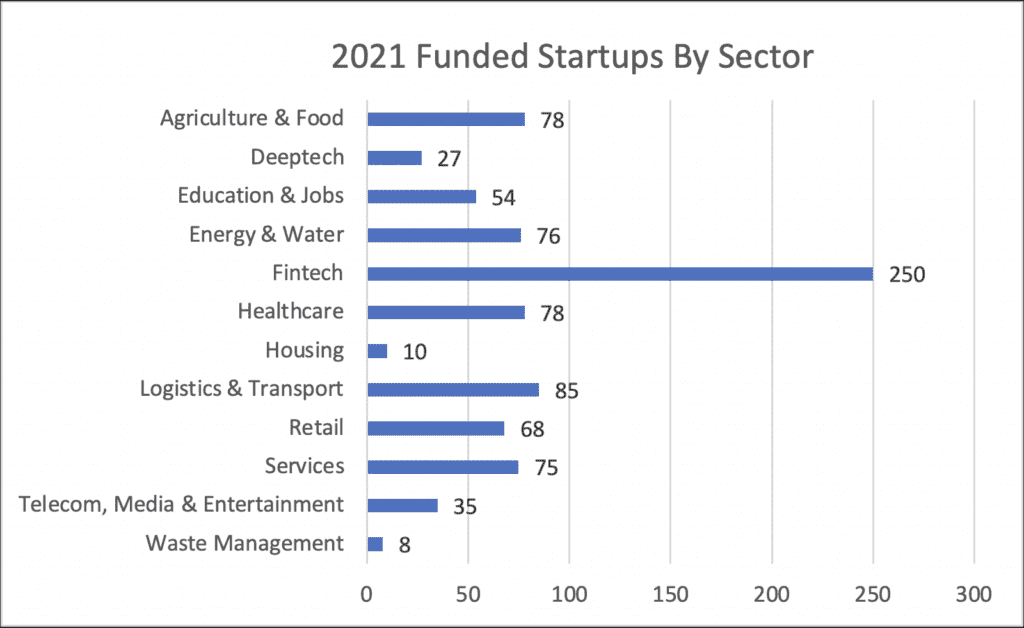
Did Investment in African Startups Accelerate in 2022?
If the second half of 2022 sees the same activity as the first half, 2022 will see 936 funded African startups. This represents an almost 10% year-over-year increase from 2021. While much of the world’s venture capital markets are reeling, Africa’s startup environment remains robust.
Which Industries Saw the Most Investment in 2022?
Between January and July 2022, 468 African startups received funding. Across the same 12 industries, Fintech continued to dominate accounting for over 31% of all funded African startups (increasing over 2% from 2021). Perhaps influenced by the Ukrainian war and related supply chain concerns, Agriculture & Food accounted for almost 7% of all funded African startups, down slightly from 2021. Telecom/Media/Entertainment accounted for approximately 3% of funded startups while Education & Jobs accounted for approximately 6%.
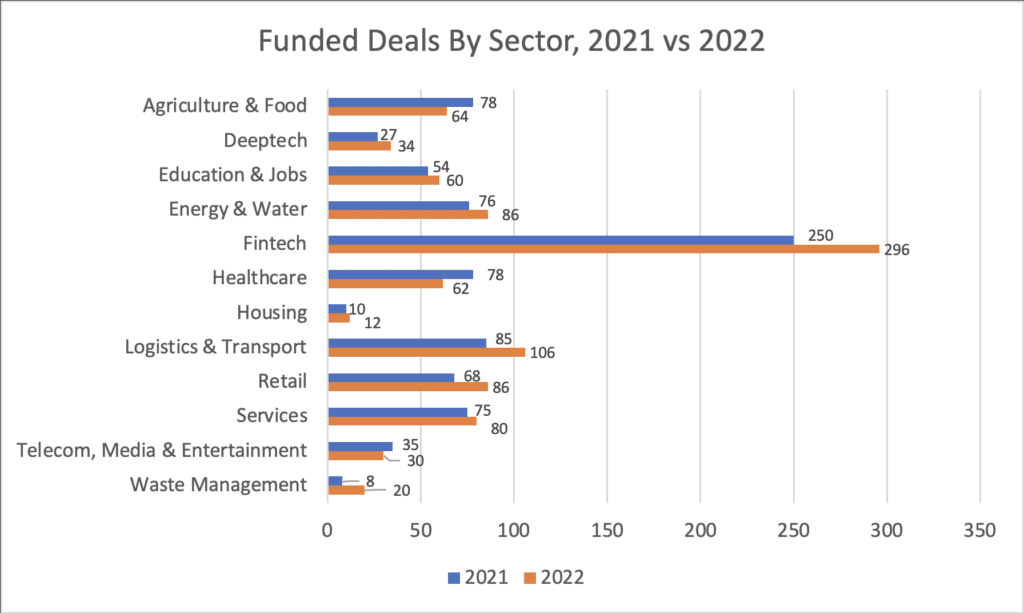
If the second half of 2022 sees the same funding activity as the first half of 2022, four out of the 12 industries would decline on a year-on-year in terms of proportionate funding across total funded investments: Services, Telecom/Media/Entertainment, Agriculture & Food, and Healthcare would decline by roughly 0.4%, 0.9%, 2.4%, and 2.6%, respectively. The industries with the largest growth are Waste Management, Retail, Logistics/Transportation, and Fintech growing roughly 1.2%, 1.2%, 1.2%, and 2%, respectively.
Where Are Most Investors Headquartered?
The database also includes information by the region of investors’ headquarters. Between January 2019 and July 2022, 1,362 startups or 33% secured funding from investors that are headquartered in Africa—the most of any region. Following Africa-headquartered investors were North American-headquartered investors 32%), European-headquartered investors (approximately 18%) and Asian-headquartered investors (8%).
In 2019, North American-headquartered investors funded more $1M+ investments in African startups than did African investors. However, the number of $1M+ investments in African startups across African, North American, European, and Asian investors only totaled 17. In 2020, the number of $500,000+ investments completed by African-headquartered investors into African startups greatly exceeded the number of investments made by North American, European, and Asian investors. 202 investments were made by African-headquartered investors. This is approximately 13% more than North American-headquartered investors, 71% more than European-headquartered investors and almost 300% more than Asian-headquartered investors.
In 2021, the number of $100,000+ investments completed by African-headquartered investors totaled to 686. North American-headquartered investors made 633 investments, roughly 8% fewer investments than African-headquartered investors. European investors made 326 investments, roughly 53% fewer investments than African-headquartered investors. Asian investors completed 172 investments, roughly 75% fewer than African-headquartered investors.
Between January and July 2022, the number of investments completed by Africa-headquartered investors was approximately equivalent to the number of investments made by North American-headquartered investors (414 by African-headquartered investors and 415 by North American-headquartered investors). European and Asian-headquartered investors completed approximately 42% and 78% fewer investments than did African-headquartered investors, respectively.
We further analyzed investment activity by North American-headquartered investors as North America is the second-most active geographical region investing in African startups (following Africa itself) between 2019 and July 2022. In 2019, during the COVID-19 pandemic, North American-headquartered investors actually completed approximately 33% more investments in African startups than did African-headquartered investors (although there were very few investments completed in 2019). In 2020, African-headquartered investors completed approximately 13% more investments than did North American-headquartered investors in African startups. In 2021, that number decreased to approximately 8%. Halfway through July 2022, African and North American-headquartered investors are completing approximately the same number of investments into African startups.
The relationship year-over-year between the number of investments completed by African versus North American-headquartered investors in African startups underpins the notion that, overall, Africa is becoming an increasingly important investment destination. Not only is the number of startups established in Africa growing, but there are also more and more African startups being funded by both African investors and North American-headquartered investors. We believe that interest from investors headquartered in other regions will, likewise, grow.
Conclusion
Multiple compelling macro trends underpin Africa’s increased startup funding. The UN Conference on Trade and Development noted that between 2006 and 2011, Africa had the highest rate of return on inflows of Foreign Direct Investment: 11% (compared to 9% in Asia, 9% in Latin America and the Caribbean, and 7% globally). Although operating from smaller bases, Africa has six of the world’s 12 fastest-growing countries: Ethiopia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Mozambique, Tanzania, and Rwanda. Africa’s population is expected to quadruple from 1.19 billion in 2015 to over 4 billion by 2100. The continent’s youthful population provides a globally attractive labor force: Africa’s average minimum wage rate has been reported as just under 50 cents per hour compared to over $10 in the UK, over $7 in the USA and over $6 in Japan. Africa’s natural resource deposits are vast. It has 60% of the world’s uncultivated arable land. Given these trends, growing innovation, and an expanding startup ecosystem, Africa is likely to see a continuation of its favorable startup funding trends for the foreseeable future.
President, CEO and Co-Founder, 1K Africa
Co-Founder & Chairman, Family Legacy Capital Credit Management, LLC (FLC Credit) & Family Legacy Capital Management, LLC (FLC)
DISCLAIMER:
The opinions and views expressed herein are solely those of the author and do not necessarily represent the view(s) of any affiliated institution or organization including without limitation 1K Africa, Family Legacy Capital Credit Management, LLC, Family Legacy Capital Management, LLC, and any investment fund, entity or vehicle managed by or affiliated or associated with any of them.

